Start a Virtual Lab
netlab up is a high-level command that:
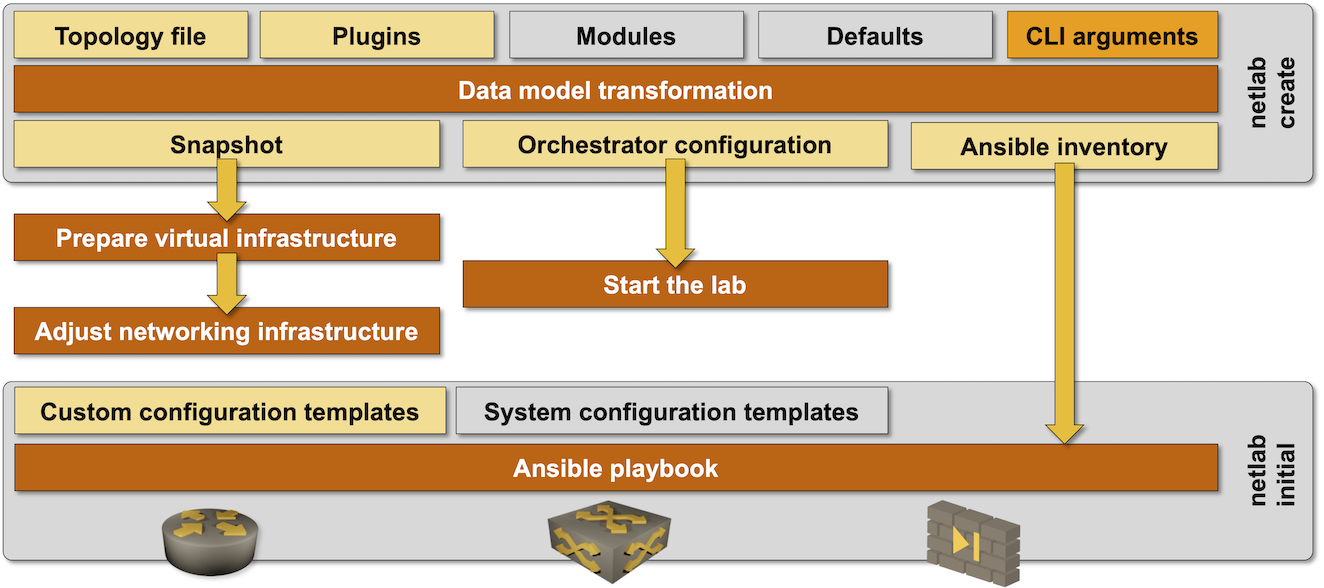
Uses netlab create to create virtualization provider configuration file, transformed topology snapshot, and network automation configuration files (Ansible inventory).
Tip
You can skip this step and reuse existing configuration files with the --snapshot flag (more details);
Checks the virtualization provider installation;
Creates the lab management network (more details)
Starts the virtual lab using the selected virtualization provider;
Performs provider-specific initialization (more details)
Deploys device configurations with netlab initial command unless it was started with the
--no-configflag, or reloads saved configurations if it was started with the--reload-configflag.
After configuring the lab with netlab initial, netlab up displays the help message defined in the lab topology.
Usage
You can use netlab up to create configuration files and start the lab, or use netlab up --snapshot to start a previously created lab or restart a lab after a server reboot (more details) using the transformed lab topology stored in the netlab.snapshot.pickle snapshot file.
usage: netlab up [-h] [--log] [-v] [-q] [--defaults [DEFAULTS ...]] [-d DEVICE]
[-p PROVIDER] [--plugin PLUGIN] [-s SETTINGS] [--no-config] [-r RELOAD]
[--no-tools] [--dry-run] [--fast-config] [--snapshot [SNAPSHOT]]
[topology]
Create configuration files, start a virtual lab, and configure it
positional arguments:
topology Topology file or URL (default: topology.yml)
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--log Enable basic logging
-v, --verbose Verbose logging (add multiple flags for increased verbosity)
-q, --quiet Report only major errors
--defaults [DEFAULTS ...]
Local topology defaults file
-d DEVICE, --device DEVICE
Default device type
-p PROVIDER, --provider PROVIDER
Override virtualization provider
--plugin PLUGIN Additional plugin(s)
-s SETTINGS, --set SETTINGS
Additional parameters added to topology file
--no-config Do not configure lab devices
-r RELOAD, --reload-config RELOAD
Reload saved configurations from specified directory
--no-tools Do not start the external tools
--dry-run Print the commands that would be executed, but do not execute
them
--fast-config Use fast device configuration (Ansible strategy = free)
--snapshot [SNAPSHOT]
Use netlab snapshot file created by a previous lab run
Tip
You can specify the lab topology with a URL. The contents from the specified URL will be downloaded, saved into downloaded.yml, and used as the lab topology.
The lab topology downloaded from a URL must be self-contained. Any external files it needs must be embedded in the lab topology with the files plugin.
Tip
The netlab up command supports comprehensive debugging implemented within the netlab create command. See netlab create documentation for more details.
Warning
Do not use the --fast-config option with custom configuration templates that must be executed in a specific order. See netlab initial documentation for more details.
Conflict Resolution
netlab up command checks the netlab status file (default: ~/.netlab/status.yml) to verify that the current lab instance (default: default) is not running in another directory. You cannot start two copies of the same lab instance (even if they use different directories) due to potential management MAC/IP address overlap. If you want to run multiple lab instances on the same server, use the multilab plugin.
netlab up command also uses the netlab.lock file in the current directory before invoking the netlab create process to ensure you cannot accidentally overwrite provider configuration files. If you want to resume a failed lab startup process (usually caused by VM timeouts), use the netlab up –snapshot command, which skips the netlab create process.
Tip
netlab up –dry-run command recreates the configuration files and cannot be used in a directory with a running lab. Use netlab up –snapshot –dry-run to display the commands used to start the lab.
Reloading Saved Configurations
When started with the --reload-config flag, netlab up tries to load device configurations saved with a previous netlab collect command to the newly-started lab devices.
The process should work (relatively) flawlessly on traditional network devices that use a single configuration file. However, do keep in mind these caveats:
Saved device configurations don’t replace startup device configurations; they are merged with them.
IP addresses (including management IP addresses) are hardcoded in the saved device configurations. Any change to the topology file, user defaults, system defaults, or netlab up CLI parameters can change device configurations. Restoring saved configurations after such a change will probably break the lab.
There are also numerous device-specific caveats:
Only the FRRouting configuration is restored on Cumulus Linux and FRR. netlab executes initial device configuration on these devices to set up interfaces and enable FRRouting daemons.
The initial state of Cisco IOS interfaces is shutdown, but the saved configuration does not include the no shutdown command. netlab executes the initial configuration on Cisco IOS/IOS-XE devices to enable the interfaces.
Restarting a Lab after a Server Reboot
You can use the netlab up --snapshot command to restart a lab after a server crash, power failure, or reboot.
The command will power up the existing Vagrant virtual machines, recreate networking components, and restart the containers (including the VM-in-container vrnetlab containers).
The restarted virtual machines will start with the saved startup configuration (assuming you saved the configuration before the crash), allowing you to skip the initial configuration process with the netlab up --snapshot --no-config command.
netlab cannot recreate the container configurations. While starting the lab, you can reload the configuration with the netlab up --snapshot --reload command if you previously collected it with the netlab collect command.
Provider-Specific Initialization
netlab up can execute provider-specific tasks before invoking the orchestration tool (Vagrant or containerlab) or after the virtual lab has been created
Tasks executed before the lab is started
When used with clab provider, netlab up creates Open vSwitch bridges or standard Linux bridges needed to implement multi-access networks.
When used with libvirt provider, netlab up creates the vagrant-libvirt management network
Tasks executed after the lab creation is completed
When used with libvirt provider, netlab up sets the
group_fwd_maskfor all Vagrant-created Linux bridges to enable LLDP passthrough.