Create Lab Configuration Files
The netlab create command reads network topology description in YAML format, performs data transformation from high-level data model to devices-and-links data model, and creates virtualization- and automation configuration files needed to set up your lab.
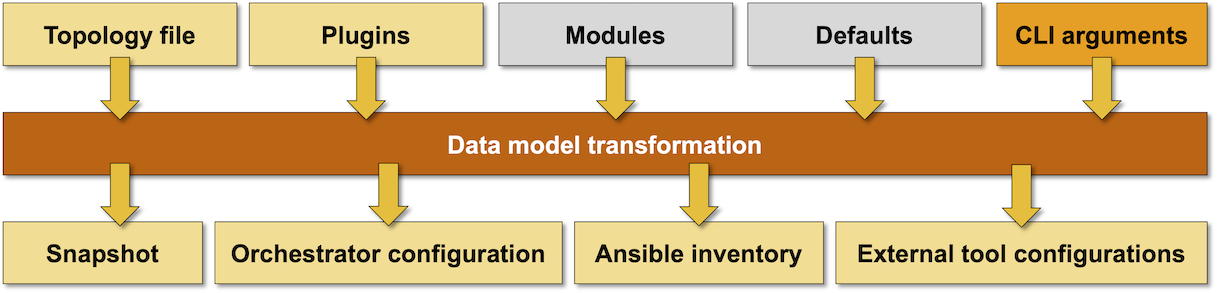
Network Topology Sources
netlab create uses these sources of information to build the desired lab topology:
Network topology in YAML format (default:
topology.yml, but see also Version-Specific Lab Topology Files)Default settings that can be specified in project-, user- or system default files
Data Model Transformation
After reading the network topology, netlab create performs a complex data transformation to generate device- and link-level data structures that fully describe the network topology, IP addressing, and (optionally) routing protocols and data-plane features.
You can influence the data model transformation with optional configuration modules and custom plugins.
Creating Configuration Files
netlab create uses transformed node- and link-level data structures to create:
Pickled transformed topology data in the netlab.snapshot.pickle file. This file is used by many other netlab commands to get the information about the currently running lab topology.
Device configuration files
Vagrantfile supporting libvirt environment
clab.yml file used by containerlab.
Ansible inventory[1], either as a single-file data structure, or as a minimal inventory file with data stored primarily in host_vars and group_vars
YAML or JSON representation of transformed lab topology or parts of the transformed data model
Configuration files for external tools
Warning
netlab create command refuses to create provider configuration files, Ansible inventory, or netlab.snapshot.pickle file if it finds netlab.lock file in the current directory.
netlab.lock file is created by the netlab up command to ensure subsequent netlab create commands don’t overwrite the provider configuration files. It is automatically removed when the netlab down command successfully stops the lab.
The Output Formats section describes how you can control the output files and their format with CLI parameters. See Output Formats for more details on individual file formats.
Usage
usage: netlab create [-h] [--log] [-q] [-v] [--defaults DEFAULTS] [-d DEVICE]
[-p PROVIDER] [-s SETTINGS] [--plugin PLUGIN]
[-o OUTPUT] [topology]
Create provider- and automation configuration files
positional arguments:
topology Topology file or URL (default: topology.yml)
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--log Enable basic logging
-q, --quiet Report only major errors
-v, --verbose Verbose logging
--defaults DEFAULTS Local topology defaults file
-d DEVICE, --device DEVICE
Default device type
-p PROVIDER, --provider PROVIDER
Override virtualization provider
--plugin PLUGIN Additional plugin(s)
-s SETTINGS, --set SETTINGS
Additional parameters added to topology file
-o OUTPUT, --output OUTPUT
Output format(s): format:option=filename
--devices Create provider configuration file and netlab-devices.yml
output files created when no output is specified:
* Pickled transformed data in netlab.snapshot.pickle
* Device configuration files
* Virtualization provider file with provider-specific filename
(Vagrantfile or clab.yml)
* Ansible inventory file (hosts.yml) and configuration (ansible.cfg)
For a complete list of output formats please consult the documentation
For more details on the topology file format, please read the lab topology overview and reference documentation.
Usage tips:
You can specify the lab topology with a URL. The contents from the specified URL will be downloaded, saved into
downloaded.yml, and used as the lab topology.
Tip
The lab topology downloaded from a URL must be self-contained. Any external files it needs must be embedded in the lab topology with the files plugin.
The netlab create command supports comprehensive debugging options. Use the
--debugCLI argument to troubleshoot topology transformation, addressing, module processing, and more.
Output Formats
Without specifying the output format(s), netlab create creates a snapshot of transformed lab topology, device configurations, a provider configuration file (Vagrantfile or clab.yml), Ansible inventory data (hosts.yml, ansible.cfg, host_vars, group_vars), and netlab-devices.yml file (if the --devices flag was specified).
You could specify one or more output formats with the -o CLI parameter. For more details, see the output formats documentation.
Tip
Use the defaults.netlab.create.output topology default to change the default output formats. Use the netlab defaults netlab.create.output command to display the current default output formats (hint: None value means “use this output format with no extra options”, setting a value to False means “do not use this output format”).
Setting Topology Parameters from Command Line
The following CLI flags can be used to change individual topology parameters:
-dsets default device type (defaults.device)-psets virtualization provider (provider)-suses thekey=valueformat to set the specified topology element’s value. The key could be a hierarchical dotted name.--pluginspecifies additional plugins not listed in lab topology or system defaults (example: multilab plugin)
Example
Assume the following topology file that uses containerlab provider to set up a lab of three Cumulus VX devices:
defaults:
device: cumulus
provider: clab
module: [ ospf ]
nodes: [ s1, s2, s3 ]
links: [ s1-s2, s2-s3 ]
When running…
$ netlab create -d iosv -p libvirt -s ospf.area=123
… you’ll get a Vagrant file using vagrant-libvirt plugin that will create a lab with three Cisco IOS routers. OSPF configuration of those routers will use area 123.
Setting Node Parameters
The --set CLI parameter can set a scalar value (number, string, True/False) anywhere within the topology file dictionary hierarchy but cannot set parameters within lists. If you want to set parameters for individual nodes you have to use the dictionary format of the nodes top-level element.
Example: Assume you want to test OSPF interoperability between Cumulus Linux and other device types. Create a topology file as above, but specify nodes as a dictionary:
defaults:
device: cumulus
module: [ ospf ]
nodes:
s1:
s2:
s3:
links: [ s1-s2, s2-s3 ]
Now you can use the --set nodes.sx.device CLI parameter to change the device type of any node in the lab. To change S1 to Cisco IOS, use:
$ netlab up -s nodes.s1.device=iosv