Containerlab Utilities
netlab clab performs these containerlab-related functions:
tarball – creates a tar archive that can recreate the lab in a vanilla containerlab environment without netlab.
build – builds a Docker container for a routing daemon. You can use such containers (together with user-defined configuration files) as images for Linux devices running under containerlab.
cleanup – removes running containers and prunes Docker system resources. You can use this command to recover from unexpected netlab- or containerlab failures.
Building a Containerlab Distribution
The netlab clab tarball command:
Collects device configurations from the current lab
Creates a new copy of containerlab configuration file (clab.config.yml) that contains pointers to startup configurations
Creates a tar archive containing clab.config.yml and related device configurations.
You can use this command only after starting a containerlab-only lab topology with devices that support the startup-config containerlab parameter.
You can use the tar archive created by the netlab clab tarball to recreate the lab in a containerlab environment without installing netlab.
$ netlab clab tarball -h
usage: netlab clab tarball [-h] [-v] [-q] [--config [OUTPUT]] [--cleanup] tarball
Create a tar archive from the current clab/device configuration
positional arguments:
tarball Destination tarball (.tar.gz will be added if needed)
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-v, --verbose Verbose logging
-q, --quiet Run Ansible playbook and tar with minimum output
--config [OUTPUT] Startup configuration directory (default: config)
--cleanup Clean up config directory and modified configuration file after
creating tarball
Building a Docker Container
netlab package includes Dockerfiles for several well-known routing daemons. You can use the netlab clab build image command to build a Docker container running the specified routing daemon.
$ netlab clab build -h
usage: netlab clab build [-h] [-l] [-t TAG] [image]
Build a routing daemon Docker container
positional arguments:
image Routing daemon name
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-l, --list List available routing daemons
-t TAG, --tag TAG Specify a non-default tag for the container image
For example, use netlab clab build bird to build the netlab/bird:latest container:
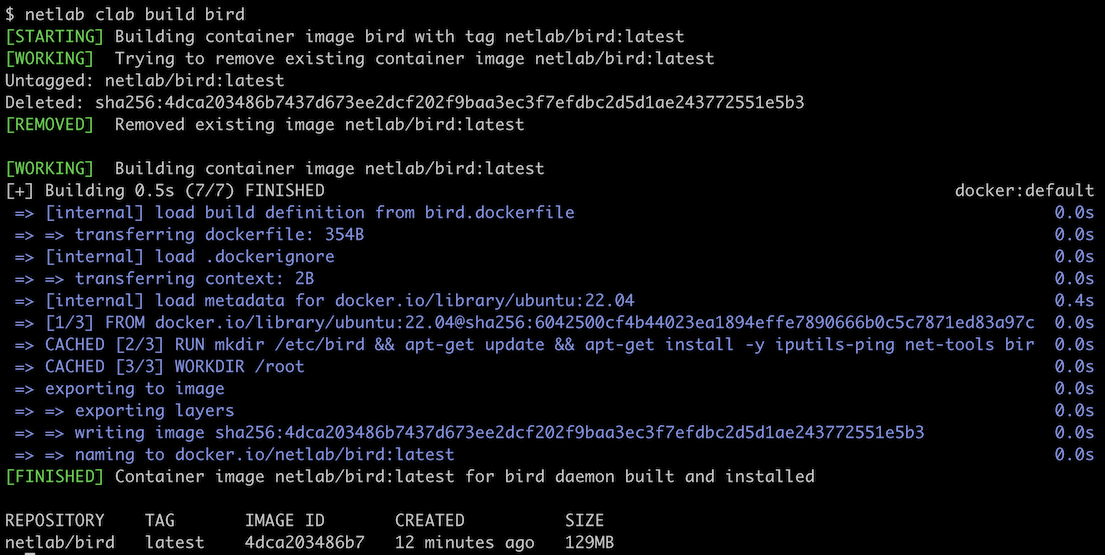
To list the available Dockerfiles, use the netlab clab build –list command:
$ netlab clab build -l
The 'netlab clab build' command can be used to build the following container images
┏━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┓
┃ daemon ┃ default tag ┃ description ┃
┡━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┩
│ bird │ netlab/bird:latest │ BIRD Internet Routing Daemon (bird.network.cz) │
│ bird.v3 │ netlab/bird.v3:latest │ BIRD Internet Routing Daemon (bird.network.cz) v3 │
│ dnsmasq │ netlab/dnsmasq:latest │ dnsmasq DHCP server │
└─────────┴───────────────────────┴───────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
For some daemons, you can build containers using different versions of that daemon. To use a non-default version of the daemon, you can:
Specify the default container tag with the
--tagparameter, for example:
$ netlab clab build bird.v3 --tag netlab/bird:latest
Change the container image with the image node parameter or the defaults.daemons.daemon.clab.image default setting.
Docker Cleanup
Containerlab might refuse to bring down a lab when it encounters containers in an unexpected state, preventing netlab down from bringing down a container-based lab. Alternatively, forcing a lab shutdown with netlab down –force might result in dangling containers or Docker networks.
The easiest way to recover from these situations is to clean up the Docker containers and related objects manually. The netlab clab cleanup provides a convenient wrapper around the docker kill and docker system prune commands.
$ netlab clab cleanup -h
usage: netlab clab cleanup [-h] [-f]
Remove running containers and Docker networks
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-f, --force Perform the cleanup without asking for confirmation